How to Calculate the Position of a Falling Object
Shae1st finds kinetic energy of a falling object using the kinematic equations to determine velocity and then kinetic energy equation. Substituting the identified values of a a and t t gives.
X 1 2 a t 2.

. T is the time in seconds. The value for g on Earth is 98 mss. During an impact an objects energy is converted into work.
Her results show that. In case you want the average V over the fall its half that. H t 16 t 2 v 0 t h 0.
In this example we will use the time of 8 seconds. Find the free fall distance using the equation s 12gt² 05 980665 8² 3138 m. X 1 2 at2.
It can be done with the help of a simple experiment if you know the distance that the object covers. Because we only consider the acceleration due to gravity in this problem the speed of a falling object depends only on its initial speed and its vertical position relative to the starting point. Draw a graph of position y as a function of time 1.
Position of a falling object Power Function Table 2. Let us consider what happens to a body as it falls from rest at a low speed through the air. You dont need to calculate the actual Kinetic Energy the body has on impact - just equate the work done by gravity with the work done on the air bag.
Since the initial position and velocity are both zero this simplifies to. However if you want to calculate the time an object takes while falling down. The position of the ball dropped from rest measured at different times Timers Log 1 Log 5 Position y m 088 042 056 157 078 304 104 541 114 650 130 845 144 1057 162 1312 174 200 1514 2000 1.
S t v t v t 3t 2 4 Step 2. 900 X 30 F air bag X 1 so F air bag 27000N. And Im told to modify the program to compute the position of an object falling for 10 seconds using this formula.
Integrating once more gives d V o T gT 2 2. 1 Where the k 12Arhoc_sh is the bulk coefficient of the airdrag the A is the front cross section area of the body the c_sh is the aerodynamic shape coefficient of the body the rho is the medium density in which the body is falling. Take the derivative of the function s t t 3 4t.
Using Law of conservation of Energy Change in KE12mv2mgh This gives us ignoring air resistance vsqrt2gh g being acceleration due to gravity and 98ms-2 Let l and m_b be length and mass of the beam respectively. Up to 10 cash back The position of any freely falling body is determined by the initial velocity and the initial height. For example if the velocity of the rock is calculated at a height of 810 m above the starting point using the method from Figure when the initial velocity is 130 ms straight up a result of is.
The distance that a free-falling object has fallen from a position of rest is also dependent upon the time of fall. V is the vertical velocity in meterssecond ms or feetsecond fts g is the acceleration due to gravity 98 ms 2 or 32 fts 2 Since the object is moving in the direction of gravity v is a positive number. Find the absolute value.
So we can write. The rock misses the edge of the cliff as it falls back to earth. Plug the given time in this example thats t 424 seconds into the function you found in Step 1.
Since the initial velocity v i 0 for an object that is simply falling the equation reduces to. A Rock Thrown Upward. X t 05 at2 v t x a acceleration -981 ms t time in seconds 10 v initial velocity x initial position.
Let velocity of object just before the collision be equal to v. Adding v0 v 0 to each side of this equation and dividing by 2 gives. A person standing on the edge of a high cliff throws a rock straight up with an initial velocity of 130 ms.
Plug the known values into the equation to solve for the unknown x x. You must solve the Keplers equation. Since the initial velocity v i 0 for an object that is simply falling the equation reduces to.
Choose how long the object is falling. Vf g t. This can be found from the kinetic energy of the object.
For a free falling object the net external force is just the weight of the object. LeeH That V Lee gives is the final V. If h is the height measured in feet t is the number of seconds the object has fallen from an initial height h 0 with an initial velocity or speed v 0 inftsec then the model for height of a falling object is.
So taking V o 0 you get T sqrt2dg and Vsqrt2dg. For many things air resistance faced while falling down creates a force that pushes the it upwards and slows the descent speed. Substituting into the second law equation gives.
X x 0 v 0 t 1 2 a t 2. We can do a little algebra and solve for the acceleration of the object in terms of the net external force and the mass of the object. Integrating the acceleration once gives V V o g T where V o is the initial velocity presumably zero and T is the time of fall.
A W m m g m g. Calculating Position and Velocity of a Falling Object. When thinking about the impact force of a falling object you can calculate the energy of the object at its point of impact if you know the height.
Dropped from rest where g is the acceleration of gravity. Ma mdvdt mg - kv2. Calculate the final free fall speed just before hitting the ground with the formula v v₀ gt 0 980665 8 7845 ms.
For objects which move slowly relative to the air such as falling dust particles the resistive force is directly proportional to the objects velocity relative to air. The formula for determining the velocity of a falling object after a time of t seconds is. The value of depends on the shape and size of the body.
X x0 v0t 1 2at2. The above equation can be used to calculate the velocity of the object after any given amount of time when dropped from rest. A F m.
If the air bag stops his fall in 1m then the ratio of the forces will be the inverse of the ratio of the distances. The energy of a moving object is called kinetic energy and is equal to one half of the objects mass times the square of its velocity.
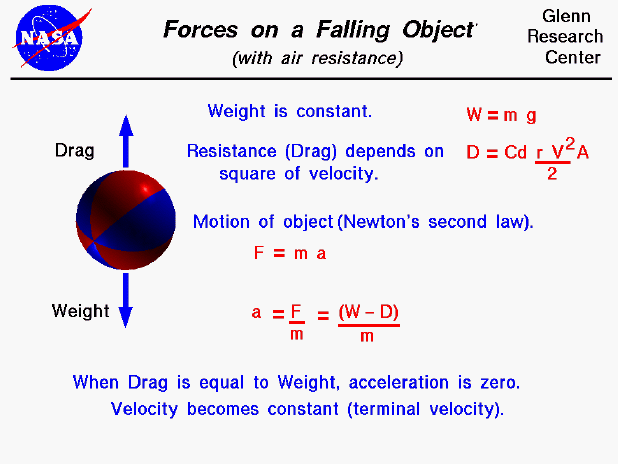
Falling Object With Air Resistance

This Image Shows How Speed Can Go To Velocity And How Velocity Can Go To Acceleration It Shows How Speed Relates To Accel Ap Calculus Physics Lessons Calculus

Free Fall Motion Maximum Height Physics Free Fall Acceleration Physics Force And Motion
Free Fall Determining How Fast And How Far

Motion Graphs Position Vs Time Graph Part 1 Acceleration Motion Graphs Physics And Mathematics Graphing

Free Fall Distance And Velocity Calculator High Accuracy Calculation

Different Equations Of Motion For Free Falling Object Teachoo
Free Falling Bodies Differential Equations Wethestudy

Different Equations Of Motion For Free Falling Object Teachoo

Conservation Of Energy Calculating The Final Velocity Of A Falling Object

Free Fall Easy Science Free Falling Easy Science Motion

Three Panels Showing Three Graphs The Top Panel Shows A Graph Of Vertical Position In Meters Versus Time In Motion Graphs Graphing Worksheets Physics Lessons




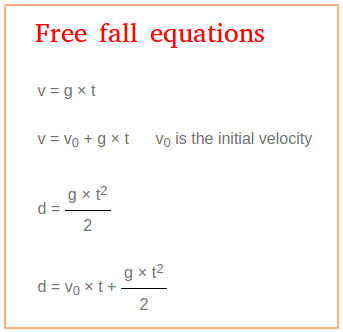
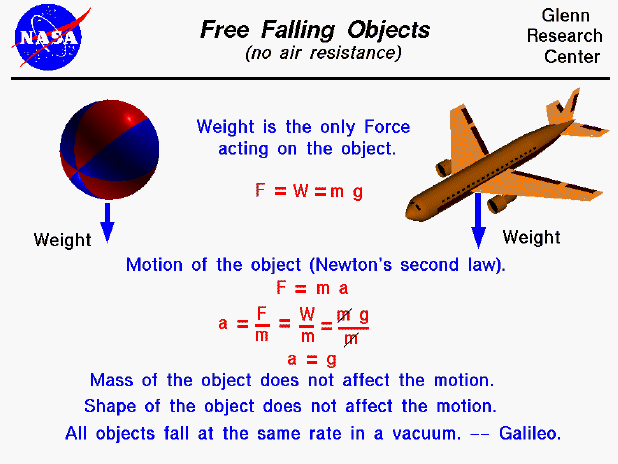


Comments
Post a Comment